請求処理の完全自動化!SaaSプロダクトの請求・決済システム実装パターンと落とし穴回避術
はじめに
この記事の要点
- SaaSの課金自動化は、成長に伴う請求業務の肥大化とヒューマンエラーを解消し、スケーラビリティを確保するために不可欠である
- 自動化の核となるのは、プラン管理、請求書発行、決済処理、入金消込の4ステップであり、これらを統合的に管理するシステムが必要となる
- Stripeなどの外部決済プラットフォームを活用することで、従量課金や定期決済、失敗時のリトライ処理などを低コストかつ安全に実装できる
- 自動化によりバックオフィス業務を80%以上削減可能となり、プロダクト開発や顧客対応といったコア業務にリソースを集中できるようになる
SaaSビジネスがスケールするにつれ、避けて通れないのが「請求業務の煩雑化」です。顧客数が増え、料金プランが多様化し、さらに従量課金や月額/年額の混在が始まると、スプレッドシートや手動での請求書発行は限界を迎え、ヒューマンエラーの温床となります。
この記事では、SaaSにおける課金業務を自動化し、ビジネスの成長を止めない堅牢なバックシステムを構築するための方法を、具体的な実装ステップとともに解説します。
SaaSの課金業務を自動化するメリットとは?
課金業務を自動化する最大のメリットは、「ミスをなくすこと」と「スケールに対応すること」です。手動での請求管理はミスが発生しやすく、未回収リスクや顧客トラブルに直結します。
- 請求書の発行漏れや金額の誤り
- 支払い期限を過ぎた顧客への督促が遅れる
- プラン変更や日割り計算が複雑で対応できない
- 財務担当者が請求処理に時間を取られ、本来の業務ができない
この記事では、SaaSプロダクトにおける請求・決済処理を完全自動化するための実装パターンと、実際の開発で遭遇する「落とし穴」を回避する方法を解説します。
SaaS請求システムとは?
SaaS請求システムは、サブスクリプションビジネスにおける以下の処理を自動化する仕組みです。
- 定期的な請求書の自動生成
- クレジットカードや銀行引き落としによる自動決済
- 支払い失敗時の自動リトライと督促
- プラン変更時の日割り計算
- 請求履歴の管理とレポート
- 税金計算と消費税対応
- インボイス制度への対応
従来の手作業では、これらすべてを人力で行う必要がありましたが、自動化することで人為的ミスを防ぎ、スケーラブルな運用が可能になります。
まとめ
この記事のポイントを簡潔にまとめます。
- 請求処理の自動化により、人為的ミスを削減しスケーラブルな運用が可能になる
- Stripe、PayPalなどの決済プラットフォームを活用することで、開発工数を大幅に削減できる
- プラン変更時の日割り計算、支払い失敗時のリトライなど、細かいエッジケースへの対応が重要
- 請求データの整合性確認と監視体制の構築により、トラブルを未然に防げる
- 段階的な実装アプローチにより、リソースが限られた組織でも導入可能
なぜ請求処理の自動化が必要なのか?
手作業の請求処理における課題
| 課題 | 影響 |
|---|---|
| 人為的ミス | 請求金額の誤り、二重請求、請求漏れが発生 |
| スケーラビリティの限界 | 顧客数が増えると処理が追いつかなくなる |
| キャッシュフローの悪化 | 督促が遅れ、未回収債権が増加 |
| 顧客体験の低下 | 請求書の遅延や誤りで信頼を失う |
| 財務担当者の負担 | 本来の分析業務に時間を割けない |
自動化によるメリット
- 正確性の向上: システムによる自動計算で誤りがなくなる
- 工数削減: 手作業の90%以上を削減可能
- 収益の最大化: 支払い失敗時の自動リトライで回収率が向上
- 顧客満足度の向上: 即座に請求書が発行され、透明性が高まる
- 事業成長への集中: 請求業務から解放され、本質的な業務に注力できる
請求・決済システムの全体アーキテクチャ
SaaSの請求システムは、以下のコンポーネントで構成されます。
システム構成
各コンポーネントの役割
| コンポーネント | 役割 | 実装例 |
|---|---|---|
| サブスクリプション管理 | プラン、価格、契約期間を管理 | Stripe Subscriptions、自社DB |
| 請求エンジン | 請求書の生成、金額計算、日割り処理 | 自社実装、Stripe Billing |
| 決済ゲートウェイ | クレジットカード決済の実行 | Stripe、PayPal、GMOペイメント |
| 請求書発行 | PDF請求書の生成と送付 | LaTeX、Puppeteer、SendGrid |
| 支払い監視 | 決済失敗の検知とリトライ | Webhook、バッチ処理 |
| 督促システム | 未払い顧客への自動通知 | メール自動送信、Slack通知 |
| レポーティング | 売上分析、未回収債権の可視化 | BI ツール、自社ダッシュボード |
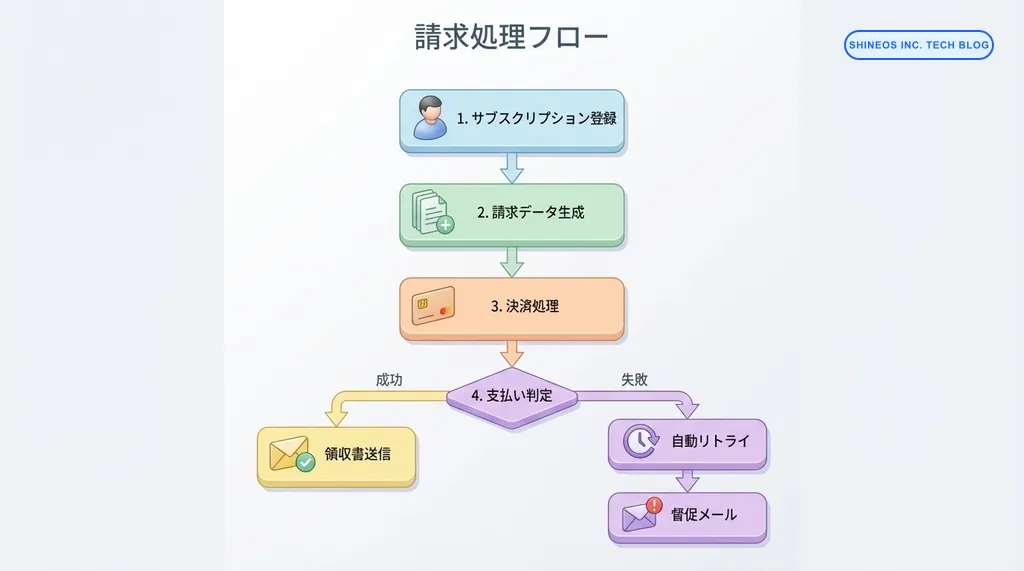
段階的な実装ステップ
完璧なシステムをいきなり作るのではなく、段階的に機能を拡張していくアプローチが現実的です。
Step 1: 基本的な定期課金の実装
まずは、最もシンプルな「毎月固定額を自動請求」から始めます。
Stripeを使った実装例:
import Stripe from 'stripe';
const stripe = new Stripe(process.env.STRIPE_SECRET_KEY!, {
apiVersion: '2023-10-16',
});
// 顧客とサブスクリプションの作成
async function createSubscription(
customerId: string,
priceId: string
) {
try {
const subscription = await stripe.subscriptions.create({
customer: customerId,
items: [{ price: priceId }],
payment_behavior: 'default_incomplete',
payment_settings: {
payment_method_types: ['card'],
save_default_payment_method: 'on_subscription',
},
expand: ['latest_invoice.payment_intent'],
});
return {
subscriptionId: subscription.id,
clientSecret: (subscription.latest_invoice as Stripe.Invoice)
.payment_intent?.client_secret,
};
} catch (error) {
console.error('サブスクリプション作成エラー:', error);
throw error;
}
}
// 使用例
const result = await createSubscription(
'cus_xxxxx', // Stripe顧客ID
'price_xxxxx' // 価格ID(例: 月額9,800円プラン)
);
console.log('サブスクリプションID:', result.subscriptionId);データベース設計:
-- サブスクリプション管理テーブル
CREATE TABLE subscriptions (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
user_id UUID NOT NULL REFERENCES users(id),
stripe_subscription_id VARCHAR(255) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
stripe_customer_id VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
plan_id UUID NOT NULL REFERENCES plans(id),
status VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, -- active, canceled, past_due
current_period_start TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
current_period_end TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
cancel_at TIMESTAMP,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW(),
updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);
-- 請求履歴テーブル
CREATE TABLE invoices (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
subscription_id UUID NOT NULL REFERENCES subscriptions(id),
stripe_invoice_id VARCHAR(255) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
amount_due INTEGER NOT NULL, -- 金額(セント単位)
amount_paid INTEGER NOT NULL,
status VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, -- draft, open, paid, void
invoice_pdf VARCHAR(500), -- PDF URL
due_date TIMESTAMP,
paid_at TIMESTAMP,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);Step 2: Webhookによる支払い状態の同期
Stripeからの通知を受け取り、データベースを最新状態に保ちます。
import { NextApiRequest, NextApiResponse } from 'next';
import Stripe from 'stripe';
import { buffer } from 'micro';
const stripe = new Stripe(process.env.STRIPE_SECRET_KEY!);
const webhookSecret = process.env.STRIPE_WEBHOOK_SECRET!;
export const config = {
api: {
bodyParser: false,
},
};
export default async function handler(
req: NextApiRequest,
res: NextApiResponse
) {
if (req.method !== 'POST') {
return res.status(405).json({ error: 'Method not allowed' });
}
const buf = await buffer(req);
const sig = req.headers['stripe-signature']!;
let event: Stripe.Event;
try {
event = stripe.webhooks.constructEvent(buf, sig, webhookSecret);
} catch (err) {
console.error('Webhook署名検証エラー:', err);
return res.status(400).json({ error: 'Invalid signature' });
}
// イベントタイプごとの処理
switch (event.type) {
case 'invoice.payment_succeeded':
await handlePaymentSucceeded(event.data.object as Stripe.Invoice);
break;
case 'invoice.payment_failed':
await handlePaymentFailed(event.data.object as Stripe.Invoice);
break;
case 'customer.subscription.updated':
await handleSubscriptionUpdated(event.data.object as Stripe.Subscription);
break;
case 'customer.subscription.deleted':
await handleSubscriptionDeleted(event.data.object as Stripe.Subscription);
break;
default:
console.log(`未処理のイベント: ${event.type}`);
}
res.json({ received: true });
}
async function handlePaymentSucceeded(invoice: Stripe.Invoice) {
// データベースを更新
await updateInvoiceStatus(invoice.id, 'paid');
// 顧客に領収書をメール送信
await sendReceiptEmail(invoice.customer as string, invoice.id);
console.log(`✅ 支払い成功: ${invoice.id}`);
}
async function handlePaymentFailed(invoice: Stripe.Invoice) {
// データベースを更新
await updateInvoiceStatus(invoice.id, 'payment_failed');
// 管理者に通知
await notifyAdminPaymentFailed(invoice);
// 顧客に支払い失敗を通知
await sendPaymentFailedEmail(invoice.customer as string);
console.error(`❌ 支払い失敗: ${invoice.id}`);
}Webhookの注意点
- 署名検証を必ず実装し、不正なリクエストを防ぐ
- 冪等性を保つ(同じイベントが複数回送られても問題ないように)
- エラー発生時のリトライに備え、処理を軽量に保つ
Step 3: プラン変更と日割り計算
顧客がプランを変更した際の日割り計算を実装します。
async function changeSubscriptionPlan(
subscriptionId: string,
newPriceId: string,
proration: 'always_invoice' | 'create_prorations' = 'create_prorations'
) {
try {
const subscription = await stripe.subscriptions.retrieve(subscriptionId);
const updatedSubscription = await stripe.subscriptions.update(
subscriptionId,
{
items: [
{
id: subscription.items.data[0].id,
price: newPriceId,
},
],
proration_behavior: proration,
// 即座に適用するか、次回更新時にするか
billing_cycle_anchor: 'now', // または 'unchanged'
}
);
// データベースを更新
await updateSubscriptionInDB(updatedSubscription);
return updatedSubscription;
} catch (error) {
console.error('プラン変更エラー:', error);
throw error;
}
}
// 使用例: スタンダードからプレミアムへ即座にアップグレード
await changeSubscriptionPlan(
'sub_xxxxx',
'price_premium_xxxxx',
'create_prorations' // 日割り計算を有効化
);日割り計算のロジック:
function calculateProration(
oldPrice: number,
newPrice: number,
remainingDays: number,
totalDays: number
): number {
// 旧プランの残り日数分を返金
const refund = (oldPrice / totalDays) * remainingDays;
// 新プランの残り日数分を請求
const charge = (newPrice / totalDays) * remainingDays;
// 差額
return charge - refund;
}
// 例: 月額1万円から2万円へアップグレード(残り15日)
const prorationAmount = calculateProration(10000, 20000, 15, 30);
console.log(`日割り請求額: ${prorationAmount}円`); // 約5,000円Step 4: 支払い失敗時の自動リトライと督促
決済失敗時の対応を自動化します。
async function handlePaymentFailedWithRetry(invoice: Stripe.Invoice) {
const subscriptionId = invoice.subscription as string;
const customerId = invoice.customer as string;
// リトライ回数を取得
const retryCount = await getRetryCount(invoice.id);
if (retryCount < 3) {
// 3回まで自動リトライ(3日後、7日後、14日後)
const retryDelays = [3, 7, 14];
const nextRetryDays = retryDelays[retryCount];
// リトライをスケジュール
await schedulePaymentRetry(invoice.id, nextRetryDays);
// 顧客にリトライ通知
await sendRetryNotification(customerId, nextRetryDays);
console.log(`🔄 ${nextRetryDays}日後に再試行: ${invoice.id}`);
} else {
// 3回失敗したらサブスクリプションを停止
await stripe.subscriptions.update(subscriptionId, {
pause_collection: { behavior: 'mark_uncollectible' },
});
// 最終督促メール
await sendFinalNotice(customerId);
// 管理者に通知
await notifyAdminSubscriptionSuspended(subscriptionId);
console.error(`⚠️ サブスクリプション停止: ${subscriptionId}`);
}
}自動督促メールのテンプレート例:
const paymentFailedEmailTemplate = {
subject: '【重要】お支払いが確認できませんでした',
body: `
{customer_name} 様
いつも弊社サービスをご利用いただき、ありがとうございます。
残念ながら、{invoice_date} のお支払いが確認できませんでした。
お支払い金額: {amount}円
請求書番号: {invoice_number}
以下の理由が考えられます:
- クレジットカードの有効期限切れ
- 利用限度額の超過
- カード情報の不一致
{retry_days}日後に再度決済を試みますので、それまでにお支払い方法を更新していただけますと幸いです。
お支払い方法の更新: {payment_method_update_url}
ご不明な点がございましたら、お気軽にお問い合わせください。
`,
};実装時の落とし穴と回避策
実際の開発で遭遇する典型的な問題と、その対処法をご紹介します。
落とし穴1: タイムゾーンの扱い
問題: Stripeは UTC で時刻を管理しますが、顧客向けの請求書には JST で表示する必要があります。
対策:
import { format, utcToZonedTime } from 'date-fns-tz';
function formatInvoiceDate(utcTimestamp: number): string {
const date = new Date(utcTimestamp * 1000);
const jstDate = utcToZonedTime(date, 'Asia/Tokyo');
return format(jstDate, 'yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm', { timeZone: 'Asia/Tokyo' });
}落とし穴2: 請求金額の整合性
問題: Stripeとデータベースで金額が一致しないことがある。
対策:
async function verifyInvoiceIntegrity(invoiceId: string) {
const stripeInvoice = await stripe.invoices.retrieve(invoiceId);
const dbInvoice = await getInvoiceFromDB(invoiceId);
if (stripeInvoice.amount_due !== dbInvoice.amount_due) {
// 不一致を検知
await logInconsistency({
invoice_id: invoiceId,
stripe_amount: stripeInvoice.amount_due,
db_amount: dbInvoice.amount_due,
});
// Slackに通知
await sendSlackAlert(
`⚠️ 請求金額の不一致を検出: ${invoiceId}`
);
}
}落とし穴3: Webhookの冪等性
問題: 同じWebhookイベントが複数回送られてくることがある。
対策:
async function processWebhookIdempotently(event: Stripe.Event) {
const eventId = event.id;
// イベントIDをチェック
const processed = await isEventProcessed(eventId);
if (processed) {
console.log(`⏭️ 既に処理済み: ${eventId}`);
return;
}
// トランザクション内で処理
await db.transaction(async (trx) => {
// イベント処理
await handleEvent(event, trx);
// 処理済みとしてマーク
await markEventAsProcessed(eventId, trx);
});
}落とし穴4: 税金計算の複雑性
問題: 消費税率が地域や商品によって異なる場合がある。
対策:
async function calculateTax(
amount: number,
customerCountry: string,
customerState?: string
): Promise<number> {
// Stripe Taxを使用(推奨)
const taxCalculation = await stripe.tax.calculations.create({
currency: 'jpy',
line_items: [
{
amount: amount,
reference: 'subscription_fee',
},
],
customer_details: {
address: {
country: customerCountry,
state: customerState,
},
address_source: 'billing',
},
});
return taxCalculation.tax_amount_exclusive;
}モニタリングと改善
請求システムは「動いていて当たり前」が期待されるため、監視体制が重要です。
監視すべきメトリクス
interface BillingMetrics {
// 収益メトリクス
mrr: number; // 月次経常収益
arr: number; // 年次経常収益
churnRate: number; // 解約率
// 請求メトリクス
invoiceSuccessRate: number; // 請求成功率
averageCollectionTime: number; // 平均回収日数
failedPaymentCount: number; // 支払い失敗件数
// 運用メトリクス
webhookProcessingTime: number; // Webhook処理時間
reconciliationErrors: number; // 整合性エラー
}
async function calculateBillingMetrics(): Promise<BillingMetrics> {
// 実装例
const metrics = {
mrr: await calculateMRR(),
arr: await calculateARR(),
churnRate: await calculateChurnRate(),
invoiceSuccessRate: await calculateInvoiceSuccessRate(),
// ...
};
// ダッシュボードに送信
await sendToDashboard(metrics);
return metrics;
}アラート設定の例
const alertThresholds = {
invoiceSuccessRate: 95, // 95%未満でアラート
webhookDelayMinutes: 10, // 10分以上遅延でアラート
failedPaymentThreshold: 5, // 1時間に5件以上の失敗でアラート
};
async function checkAlertsAndNotify() {
const metrics = await calculateBillingMetrics();
if (metrics.invoiceSuccessRate < alertThresholds.invoiceSuccessRate) {
await sendSlackAlert(
`🚨 請求成功率が低下: ${metrics.invoiceSuccessRate}%`
);
}
}よくある質問
Stripeを使わずに自社実装することは可能ですか?
可能ですが、PCI DSS準拠のためのセキュリティ要件が非常に厳しいため、推奨しません。Stripeなどの決済プラットフォームを使うことで、カード情報を自社サーバーで扱わずに済み、セキュリティリスクを大幅に削減できます。
請求書の PDF 生成はどうすれば良いですか?
以下の選択肢があります。
- Stripe Invoice PDF: Stripeが自動生成するPDFを使用(最も簡単)
- Puppeteer: HTMLをPDFに変換(カスタマイズ性が高い)
- LaTeX: 高品質なPDFを生成(複雑だが美しい)
スタートアップではStripeのPDFで十分なケースが多いです。
請求失敗時のリトライは何回が適切ですか?
一般的には 3-4回 が推奨されます。リトライ間隔は、3日後 → 7日後 → 14日後のように徐々に長くします。それ以上はキャッシュフローへの悪影響が大きいため、サブスクリプションを一時停止し、手動での支払いを促すのが現実的です。
インボイス制度への対応はどうすれば良いですか?
2023年10月から日本で開始されたインボイス制度では、適格請求書に以下の情報が必要です。
- 登録番号(T + 13桁)
- 取引年月日
- 取引内容
- 税率ごとの合計額
- 消費税額
Stripeを使う場合、tax_idに登録番号を設定することで対応できます。
await stripe.customers.update(customerId, {
tax_exempt: 'none',
tax_ids: [{ type: 'jp_trn', value: 'T1234567890123' }],
});おわりに
SaaSビジネスにおける請求・決済処理の自動化は、事業のスケーラビリティを確保する上で欠かせない要素です。手作業での請求処理から脱却することで、人為的ミスを削減し、本質的な事業成長に集中できるようになります。
実装においては、Stripeなどの決済プラットフォームを活用することで開発工数を大幅に削減できます。ただし、Webhook処理の冪等性確保、タイムゾーンの扱い、請求データの整合性確認など、細部への配慮が重要です。
最初から完璧なシステムを目指すのではなく、基本的な定期課金から始めて、段階的に機能を拡張していくアプローチが成功の鍵となります。
私たちShineosでは、SaaS プロダクトの請求・決済システム構築を支援しています。Stripe連携からカスタムロジックの実装、既存システムとの統合まで、トータルでサポートいたします。ご興味のある方は、ぜひお気軽にご相談ください。