Function Callingを活用したLLMアプリケーション開発 - 外部ツール連携の実践パターン
はじめに
この記事の要点
- Function Callingは、LLMがユーザーの意図を解釈し、適切な外部APIや関数を構造化データで呼び出すための機能である
- リアルタイムデータの取得、データベース操作、複雑な計算など、LLM単体では不可能な「実行」を伴うタスクを実現できる
- 関数スキーマ(JSON)の定義、パラメータ抽出、関数実行、結果のLLMへの返却という一連のサイクルで動作する
- 明確な関数の説明(description)、厳格なパラメータバリデーション、タイムアウト設定などのエラーハンドリングが本番運用の鍵となる
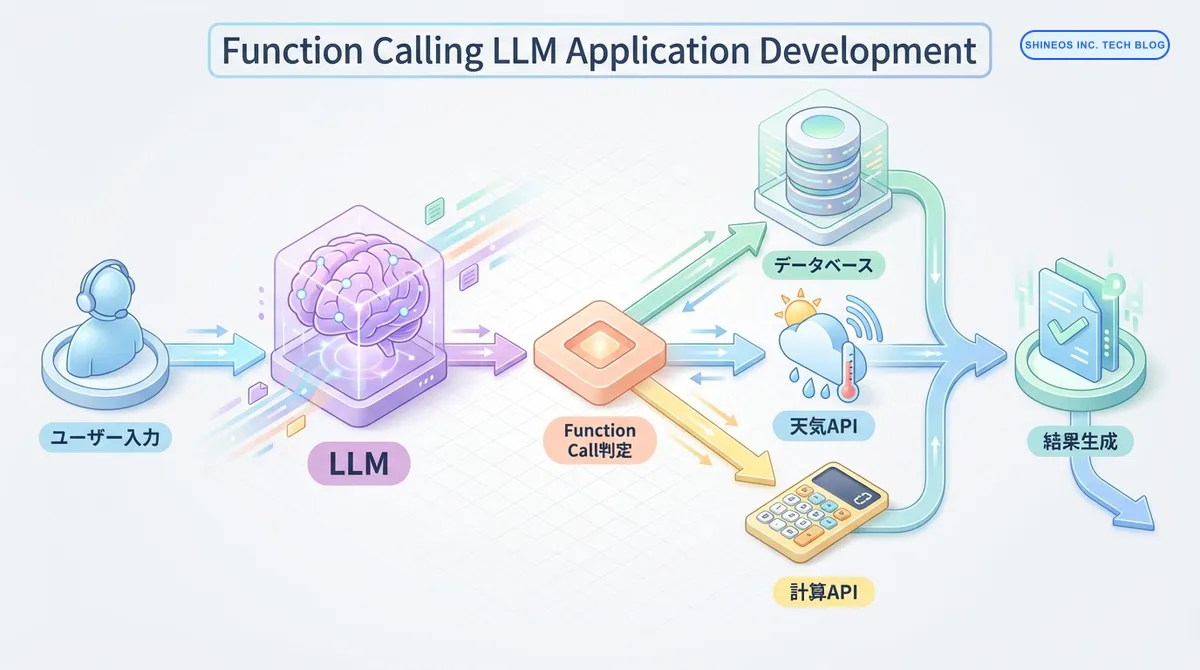
LLM(大規模言語モデル)を活用したアプリケーション開発において、外部ツールやAPIとの連携は重要な機能です。OpenAIのGPT-4やAnthropicのClaudeなど、主要なLLMは Function Calling(関数呼び出し)機能を提供しており、これによりLLMが自然言語の指示を構造化されたAPI呼び出しに変換できます。
この記事では、Function Callingの基本概念から実践的な実装パターンまで、実務で活用できる知識を体系的に解説します。
対象読者: LLMアプリケーション開発者、バックエンドエンジニア、AI活用を検討している技術リーダー
Function Callingとはどのような機能ですか?
Function Calling(関数呼び出し)は、LLMが外部の関数やAPIを呼び出すための機能です。ユーザーの自然言語入力を解析し、適切な関数とそのパラメータを自動的に判定します。
従来のLLMは、テキスト生成に特化していましたが、Function Callingにより以下が可能になりました:
- 外部データベースへのクエリ実行
- 天気情報やニュースなどのリアルタイムデータ取得
- 計算処理や複雑なビジネスロジックの実行
- 複数のAPIを組み合わせた複雑なワークフローの実現
まとめ
以下の表で、Function Callingの主要な概念を整理します:
| 項目 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| Function Schema | 関数の仕様を定義したJSON形式のメタデータ(関数名、説明、パラメータ) |
| パラメータ抽出 | ユーザー入力から必要なパラメータをLLMが自動的に抽出 |
| 関数選択 | 複数の利用可能な関数から、最適なものをLLMが判定 |
| 実行フロー | ユーザー入力 → LLM判定 → 関数実行 → 結果をLLMに返却 → 最終レスポンス生成 |
| 主な用途 | データベース検索、外部API連携、計算処理、ファイル操作 |
Function Callingの実行フロー
Function Callingは以下のステップで実行されます:
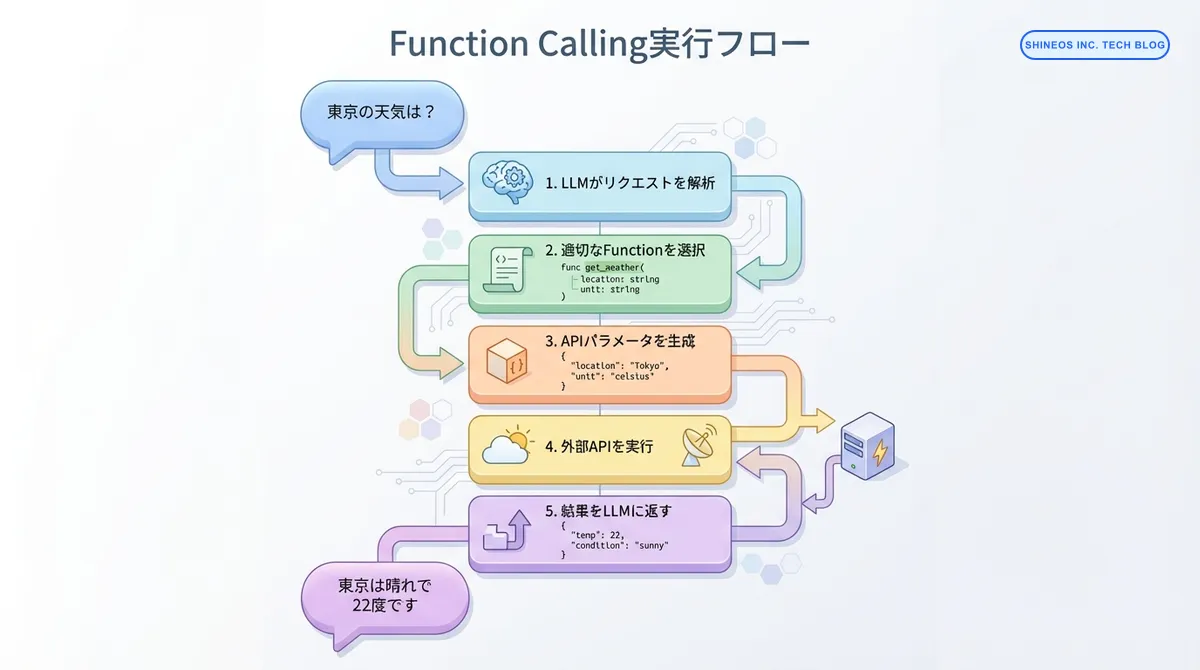
- ユーザー入力の解析: LLMがユーザーのリクエストを理解
- 適切な関数の選択: 利用可能な関数の中から最適なものを判定
- パラメータの生成: 関数実行に必要なパラメータをJSON形式で生成
- 外部APIの実行: アプリケーション側が実際の関数を実行
- 結果の返却: 実行結果をLLMに返し、自然言語レスポンスを生成
Function Schemaの定義
Function Callingを使用するには、まず関数の仕様(スキーマ)を定義します。スキーマには関数名、説明、パラメータの型情報が含まれます。
Python(OpenAI SDK)の実装例
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
# 天気情報取得関数のスキーマ定義
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "指定された都市の現在の天気情報を取得します",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "都市名(例:東京、大阪)"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"description": "温度の単位"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
}
]TypeScript(OpenAI SDK)の実装例
import OpenAI from 'openai';
const openai = new OpenAI();
// データベース検索関数のスキーマ定義
const tools: OpenAI.Chat.ChatCompletionTool[] = [
{
type: "function",
function: {
name: "search_database",
description: "データベースから顧客情報を検索します",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
customer_id: {
type: "string",
description: "顧客ID"
},
include_orders: {
type: "boolean",
description: "注文履歴を含めるかどうか"
}
},
required: ["customer_id"]
}
}
}
];実践的な実装パターン
パターン1: 単一関数呼び出し
最もシンプルなパターンです。1つの関数を定義し、ユーザーの質問に応じて実行します。
import json
def get_weather(location: str, unit: str = "celsius") -> dict:
"""天気情報を取得する関数(実際はAPIを呼び出す)"""
# 実際の実装ではWeather APIを呼び出す
return {
"location": location,
"temperature": 22,
"condition": "sunny",
"unit": unit
}
# LLMに関数を提供してリクエスト
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "東京の天気を教えて"}
],
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto" # 自動判定
)
# Function Callingが必要かチェック
if response.choices[0].message.tool_calls:
tool_call = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0]
function_name = tool_call.function.name
function_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# 関数を実行
if function_name == "get_weather":
result = get_weather(**function_args)
# 結果をLLMに返して最終レスポンス生成
second_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "東京の天気を教えて"},
response.choices[0].message,
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": json.dumps(result)
}
]
)
print(second_response.choices[0].message.content)
# 出力例: "東京は現在晴れで、気温は22度です。"パターン2: 複数関数の動的選択
複数の関数を定義し、LLMが状況に応じて適切な関数を選択します。
// 複数の関数を定義
const available_functions = {
get_weather: (location: string) => {
// 天気API呼び出し
return { temp: 22, condition: "sunny" };
},
search_product: (query: string) => {
// 商品検索API呼び出し
return { products: [{ name: "商品A", price: 1000 }] };
},
calculate: (expression: string) => {
// 計算実行
return { result: eval(expression) };
}
};
const tools = [
// get_weather, search_product, calculate のスキーマ定義
// ...省略
];
async function runConversation(userMessage: string) {
const messages = [{ role: "user", content: userMessage }];
const response = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4",
messages: messages,
tools: tools,
tool_choice: "auto"
});
const responseMessage = response.choices[0].message;
// Function Callingの処理
if (responseMessage.tool_calls) {
for (const toolCall of responseMessage.tool_calls) {
const functionName = toolCall.function.name;
const functionArgs = JSON.parse(toolCall.function.arguments);
// 関数実行
const functionToCall = available_functions[functionName];
const functionResponse = functionToCall(...Object.values(functionArgs));
// 結果を追加
messages.push(responseMessage);
messages.push({
role: "tool",
tool_call_id: toolCall.id,
content: JSON.stringify(functionResponse)
});
}
// 最終レスポンス生成
const finalResponse = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4",
messages: messages
});
return finalResponse.choices[0].message.content;
}
return responseMessage.content;
}
// 使用例
const result = await runConversation("東京の天気と、100 * 50の計算結果を教えて");
console.log(result);
// 出力例: "東京は晴れで22度です。また、100 × 50 = 5000です。"パターン3: 連鎖的な関数呼び出し
1つの関数の結果を使って、別の関数を呼び出す連鎖的なワークフローです。
# 顧客IDから注文履歴を取得し、さらに商品詳細を取得
def get_customer_orders(customer_id: str) -> list:
"""顧客の注文履歴を取得"""
return [{"order_id": "12345", "product_id": "P001"}]
def get_product_details(product_id: str) -> dict:
"""商品詳細を取得"""
return {"product_id": product_id, "name": "商品A", "price": 1500}
tools = [
# get_customer_orders と get_product_details のスキーマ定義
# ...省略
]
def process_with_chain(user_query: str):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": user_query}]
while True:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=messages,
tools=tools
)
response_message = response.choices[0].message
# Function Callingが不要になったら終了
if not response_message.tool_calls:
return response_message.content
# 各関数を実行
messages.append(response_message)
for tool_call in response_message.tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
function_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# 関数実行(実際のロジック)
if function_name == "get_customer_orders":
result = get_customer_orders(**function_args)
elif function_name == "get_product_details":
result = get_product_details(**function_args)
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": json.dumps(result)
})
# 実行例
result = process_with_chain("顧客ID12345の最新注文の商品詳細を教えて")
print(result)エラーハンドリングとベストプラクティス
Function Callingを本番環境で使用する際の注意点です。
エラーハンドリングの実装
def safe_function_call(function_name: str, function_args: dict) -> dict:
"""安全な関数呼び出しのラッパー"""
try:
# タイムアウト設定
result = call_function_with_timeout(function_name, function_args, timeout=10)
return {"status": "success", "data": result}
except TimeoutError:
return {"status": "error", "message": "関数の実行がタイムアウトしました"}
except ValueError as e:
return {"status": "error", "message": f"パラメータエラー: {str(e)}"}
except Exception as e:
return {"status": "error", "message": f"予期しないエラー: {str(e)}"}ベストプラクティス
Function Calling実装時の重要ポイント
- 明確な関数説明: LLMが適切に判断できるよう、
descriptionは具体的に記述 - パラメータのバリデーション: LLMが生成したパラメータを必ず検証
- エラーハンドリング: 外部API呼び出しは失敗する前提で実装
- タイムアウト設定: 長時間実行を防ぐため、必ずタイムアウトを設定
- コスト管理: Function Calling は追加のトークンを消費するため、コスト監視が重要
パフォーマンス最適化
| 最適化項目 | 説明 | 効果 |
|---|---|---|
| 関数の絞り込み | 状況に応じて提供する関数を限定 | レスポンス速度向上、精度向上 |
| 並列実行 | 独立した複数の関数呼び出しを並列化 | 処理時間短縮 |
| キャッシング | API結果をキャッシュして再利用 | コスト削減、速度向上 |
| Streaming対応 | レスポンスをストリーミングで返却 | ユーザー体験向上 |
実務での活用例
Function Callingは、以下のような実務シーンで活用されています:
カスタマーサポート自動化
# 顧客情報検索、注文履歴確認、返金処理など複数の機能を統合
support_tools = [
{"name": "search_customer", "description": "顧客情報を検索"},
{"name": "get_order_history", "description": "注文履歴を取得"},
{"name": "process_refund", "description": "返金処理を実行"},
{"name": "send_email", "description": "顧客にメール送信"}
]ビジネスインテリジェンス
// データベースクエリ、レポート生成、グラフ作成を自然言語で実行
const bi_tools = [
{ name: "run_sql_query", description: "SQLクエリを実行" },
{ name: "generate_report", description: "レポートを生成" },
{ name: "create_visualization", description: "データ可視化を作成" }
];社内業務自動化
- 会議室予約システムとの連携
- 勤怠管理システムへの記録
- 経費精算の申請処理
- ドキュメント検索と要約
よくある質問
Function Callingのコストはどのくらいですか?
Function Calling自体は追加料金がかかりませんが、関数の定義(スキーマ)もトークンとしてカウントされます。複数の関数を定義すると、その分入力トークンが増加します。
目安として、関数1つあたり50-200トークン程度のオーバーヘッドが発生します。コスト最適化のため、必要最小限の関数のみを提供することが推奨されます。
LLMが誤った関数を選択することはありますか?
はい、Function Callingは100%の精度を保証するものではありません。特に以下の場合に誤選択が発生しやすくなります:
- 関数の説明が曖昧
- 似た機能を持つ複数の関数が存在
- ユーザー入力が不明瞭
対策として、関数のdescriptionを明確に記述し、異なる関数間で役割を明確に分離することが重要です。
実行時間が長い関数はどう扱うべきですか?
長時間実行される関数(データベースの大規模集計など)は、以下のアプローチを検討してください:
- 非同期処理: 関数をバックグラウンドで実行し、完了通知を送る
- 進捗報告: 処理状況をユーザーに定期的にフィードバック
- タイムアウト設定: 一定時間で処理を打ち切り、エラーを返す
- 事前処理: 可能な限りデータを事前集計しておく
Function Callingのタイムアウトは、OpenAI APIのタイムアウト(デフォルト600秒)とは別に、アプリケーション側で設定する必要があります。
セキュリティ面での注意点はありますか?
Function Callingを使用する際は、以下のセキュリティ対策が必要です:
- 入力検証: LLMが生成したパラメータを信頼せず、必ず検証
- 権限チェック: ユーザーの権限に応じて実行可能な関数を制限
- SQLインジェクション対策: データベースクエリには必ずプリペアドステートメントを使用
- 機密情報の保護: APIキーや個人情報を関数の戻り値に含めない
- 監査ログ: どのユーザーがどの関数を実行したか記録
おわりに
Function Callingは、LLMアプリケーションに外部システムとの連携能力を付与する強力な機能です。適切な設計とエラーハンドリングを実装することで、実務で信頼できるシステムを構築できます。
次のステップとして、以下の学習をお勧めします:
- LangChainのToolsとAgentsの活用: より高度なツール連携パターン
- マルチエージェントシステム: 複数のAIエージェントを協調させる設計
- RAGとの組み合わせ: Function Callingとベクトル検索の統合
私たちShineosでは、AIエージェントを活用した業務自動化システムの開発支援を行っています。Function Callingを活用したシステム構築にご興味がある方は、ぜひお問い合わせください。