LLMの幻覚(Hallucination)対策 - 信頼性の高いAIシステムの構築方法
はじめに
この記事の要点
- 幻覚(Hallucination)は、LLMが事実と異なる情報を正確そうに生成する現象であり、AI信頼性の最大の障壁である
- RAG(検索拡張生成)の導入により、信頼できる外部知識をLLMに提供することが最も効果的な対策となる
- 明確な制約(「わからない場合は答えない」等)を含むプロンプト設計や、出力温度の調整により発生率を抑制できる
- セルフチェックプロンプトや外部システムによる自動検証、ソース引用の徹底といった多層防御的なアプローチが推奨される
大規模言語モデル(LLM)を活用したアプリケーション開発において、最も重要な課題の1つが 幻覚(Hallucination) です。幻覚とは、LLMが事実と異なる情報を、あたかも正確な情報であるかのように生成してしまう現象を指します。
企業システムや医療、金融などの重要なドメインでLLMを活用する際、この幻覚問題への対策は必須です。本記事では、幻覚が発生する原因から、実務で使える具体的な対策手法まで、体系的に解説します。
対象読者: AI/LLMアプリケーション開発者、プロダクトマネージャー、AI活用を検討している技術リーダー
LLMの幻覚とはどのような現象ですか?
LLMの幻覚(Hallucination)とは、モデルが学習データに基づかない、または事実と異なる情報を生成する現象です。以下のような形で現れます:
- 事実の捏造: 存在しない企業名、製品名、統計データを生成
- 文脈の誤解: 質問の意図を誤解し、関連性のない回答を提供
- 時系列の混同: 古い情報と新しい情報を混同
- 論理的矛盾: 自己矛盾した説明や結論
幻覚が発生する主な原因
| 原因 | 説明 | 影響度 |
|---|---|---|
| 学習データの限界 | トレーニングデータに含まれない情報への対応 | 高 |
| 確率的生成 | 次のトークンを確率的に予測する仕組み | 中 |
| 文脈の理解不足 | 質問の意図や背景を完全に理解できない | 高 |
| 過度な一般化 | 類似パターンからの不適切な推論 | 中 |
| 曖昧なプロンプト | 不明確な指示による誤った解釈 | 高 |
まとめ
幻覚対策の主要なアプローチを整理します:
| 対策手法 | 概要 | 効果 | 実装難易度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAG統合 | 外部知識ベースから関連情報を検索して提供 | 非常に高い | 中 |
| プロンプト設計 | 明確な指示と制約を含むプロンプト | 高い | 低 |
| 出力検証 | 生成された情報を自動的に検証 | 高い | 中 |
| ソース引用 | 情報源を明示し、トレーサビリティ確保 | 中 | 低 |
| 温度パラメータ調整 | 生成の創造性を制限し正確性を向上 | 中 | 低 |
| 複数モデルの比較 | 複数のLLMの出力を比較検証 | 高い | 高 |
| 人間によるレビュー | 重要な出力を人間が確認 | 非常に高い | 低 |
幻覚対策の5つの実践的戦略
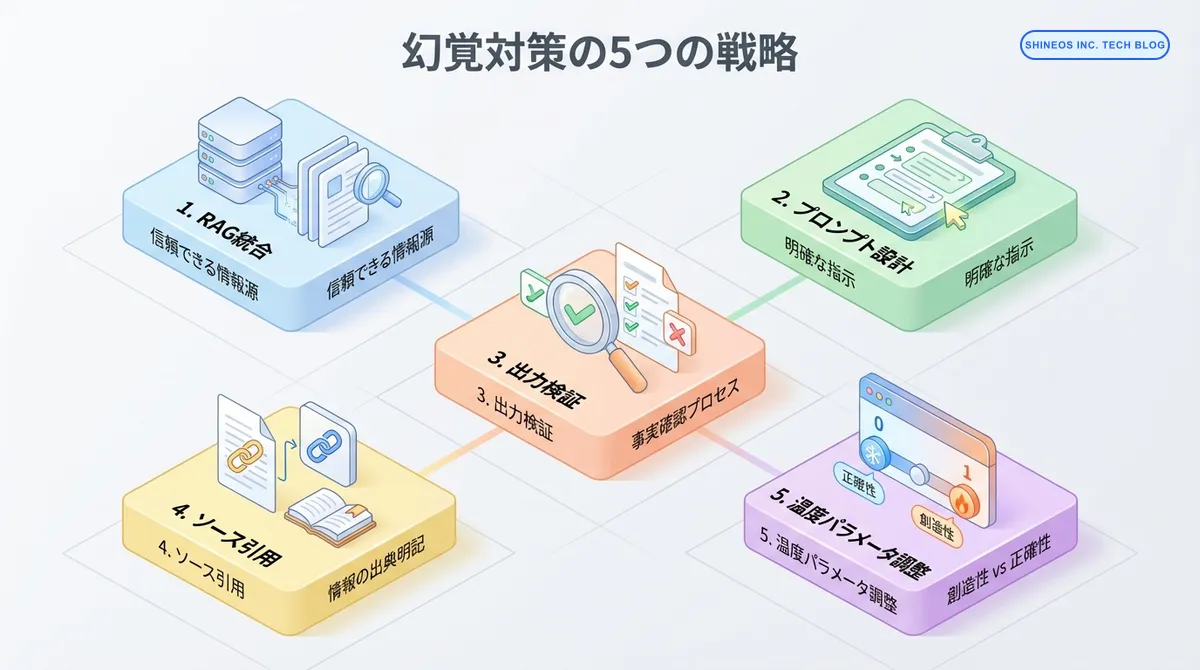
戦略1: RAG(検索拡張生成)の統合
RAGは、LLMに外部の信頼できる情報源を提供することで、幻覚を大幅に削減します。
実装例(Python + LangChain)
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
# ベクトルデータベースの構築
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=documents, # 信頼できる情報源のドキュメント
embedding=embeddings
)
# RAGチェーンの構築
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4",
temperature=0 # 正確性重視
)
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=vectorstore.as_retriever(
search_kwargs={"k": 3} # 上位3件の関連文書を取得
),
return_source_documents=True # ソース文書も返す
)
# クエリ実行
result = qa_chain({"query": "最新の製品仕様は?"})
answer = result["result"]
sources = result["source_documents"]
# ソース引用を含む回答生成
response = f"{answer}\n\n参照元:\n"
for i, doc in enumerate(sources, 1):
response += f"{i}. {doc.metadata['source']}\n"
print(response)RAG実装のベストプラクティス
RAG実装時の重要ポイント
- 高品質なデータソース: 正確で最新の情報源を使用
- 適切なチャンキング: 文書を適切なサイズに分割(200-500トークン推奨)
- メタデータの活用: 日付、出典、信頼度などのメタデータを保持
- 定期的な更新: 情報源を定期的に更新してフレッシュネスを保つ
戦略2: 効果的なプロンプト設計
プロンプトに明確な制約と指示を含めることで、幻覚を抑制します。
幻覚を減らすプロンプトパターン
# ❌ 悪い例:曖昧で制約がない
prompt = "AIについて教えて"
# ✅ 良い例:明確な制約と指示
prompt = """
以下の制約に従って回答してください:
1. 確実な情報のみを提供してください
2. 不確実な場合は「情報が不足しています」と明示してください
3. 推測や仮定を述べる場合は、その旨を明記してください
4. 具体的な数値を述べる場合は、出典を示してください
質問:AI市場の2023年の成長率は?
"""
response = llm.invoke(prompt)構造化プロンプトの実装
def create_safe_prompt(question: str, context: str = "") -> str:
"""幻覚を抑制するための構造化プロンプト生成"""
return f"""
あなたは正確性を最優先する情報アシスタントです。
【重要な制約】
- 確実な情報のみを提供してください
- わからない場合は「情報がありません」と答えてください
- 推測する場合は必ず「推測ですが」と前置きしてください
- 具体的な数値や日付には必ず出典を付けてください
【提供されている情報】
{context if context else "情報は提供されていません"}
【質問】
{question}
【回答】
"""
# 使用例
safe_prompt = create_safe_prompt(
question="当社の2023年の売上は?",
context="決算資料によると、2023年度の売上は150億円でした。"
)
response = llm.invoke(safe_prompt)戦略3: 出力の自動検証
LLMの出力を別のシステムやモデルで検証することで、幻覚を検出します。
事実検証システムの実装
from typing import Dict, List
def verify_llm_output(
output: str,
verification_sources: List[str]
) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""LLMの出力を検証する"""
# 1. 固有名詞や数値を抽出
entities = extract_entities(output)
# 2. 各エンティティを検証
verification_results = []
for entity in entities:
# データベースや外部APIで検証
is_valid = check_against_sources(entity, verification_sources)
verification_results.append({
"entity": entity,
"verified": is_valid,
"confidence": calculate_confidence(entity, verification_sources)
})
# 3. 全体の信頼度スコアを算出
overall_confidence = sum(
r["confidence"] for r in verification_results
) / len(verification_results)
return {
"output": output,
"entities": verification_results,
"overall_confidence": overall_confidence,
"is_trustworthy": overall_confidence > 0.8
}
# 使用例
llm_response = "株式会社XYZは2020年に設立され、売上は100億円です。"
verification = verify_llm_output(
output=llm_response,
verification_sources=["company_database", "financial_reports"]
)
if not verification["is_trustworthy"]:
print("警告: 出力の信頼性が低いため、人間による確認が必要です")セルフチェックプロンプト
def self_verification_chain(question: str) -> dict:
"""LLM自身に回答の検証をさせる"""
# 1. 初回回答生成
initial_response = llm.invoke(f"""
質問: {question}
できる限り正確に回答してください。
""")
# 2. 自己検証
verification_prompt = f"""
以下の回答の正確性を評価してください。
【質問】
{question}
【回答】
{initial_response}
【評価項目】
1. 事実の正確性(1-5点)
2. 根拠の明確さ(1-5点)
3. 不確実性の適切な表現(1-5点)
評価とともに、問題点があれば指摘してください。
"""
verification = llm.invoke(verification_prompt)
# 3. 必要に応じて修正
if needs_correction(verification):
corrected_response = llm.invoke(f"""
以下の指摘に基づいて回答を修正してください:
【元の回答】
{initial_response}
【指摘事項】
{verification}
【修正後の回答】
""")
return {
"final_answer": corrected_response,
"verification": verification,
"corrected": True
}
return {
"final_answer": initial_response,
"verification": verification,
"corrected": False
}戦略4: ソース引用の徹底
情報源を明示することで、ユーザーが情報の信頼性を判断できるようにします。
ソース付き回答の生成
interface SourcedAnswer {
answer: string;
sources: Source[];
confidence: number;
}
interface Source {
content: string;
url?: string;
title: string;
relevance_score: number;
}
async function generateAnswerWithSources(
question: string,
documents: Document[]
): Promise<SourcedAnswer> {
// 関連文書を検索
const relevantDocs = await searchRelevantDocuments(question, documents);
// ソース付きプロンプト生成
const prompt = `
以下の情報源のみを使用して質問に回答してください。
情報源に記載されていない内容は回答に含めないでください。
【情報源】
${relevantDocs.map((doc, i) => `
[${i + 1}] ${doc.title}
${doc.content}
`).join('\n')}
【質問】
${question}
【回答形式】
回答の各文の後に、参照した情報源の番号を [1], [2] のように記載してください。
【回答】
`;
const response = await llm.invoke(prompt);
// 引用を解析
const citations = extractCitations(response);
const citedSources = citations.map(num => relevantDocs[num - 1]);
return {
answer: response,
sources: citedSources,
confidence: calculateConfidence(citations, relevantDocs)
};
}
// 使用例
const result = await generateAnswerWithSources(
"最新の製品機能は?",
productDocuments
);
console.log(result.answer);
console.log("\n参考資料:");
result.sources.forEach((source, i) => {
console.log(`[${i + 1}] ${source.title}`);
if (source.url) console.log(` ${source.url}`);
});戦略5: パラメータ調整による制御
モデルのパラメータを調整して、正確性と創造性のバランスを取ります。
温度パラメータの最適化
def generate_with_optimal_params(
prompt: str,
task_type: str = "factual"
) -> str:
"""タスクに応じた最適なパラメータでLLMを実行"""
# タスクタイプ別のパラメータ設定
param_configs = {
"factual": {
"temperature": 0.0, # 決定的な出力
"top_p": 0.1,
"frequency_penalty": 0.0,
"presence_penalty": 0.0
},
"creative": {
"temperature": 0.8,
"top_p": 0.9,
"frequency_penalty": 0.5,
"presence_penalty": 0.5
},
"balanced": {
"temperature": 0.3,
"top_p": 0.5,
"frequency_penalty": 0.2,
"presence_penalty": 0.2
}
}
params = param_configs.get(task_type, param_configs["balanced"])
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
**params
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
# 使用例
# 事実ベースの質問には低い温度
factual_answer = generate_with_optimal_params(
"2024年の東京オリンピックの開催日は?",
task_type="factual"
)
# クリエイティブなタスクには高い温度
creative_answer = generate_with_optimal_params(
"未来の都市をイメージした物語を書いて",
task_type="creative"
)実務での幻覚対策フレームワーク
複数の対策を組み合わせた包括的なフレームワークです。
from typing import Dict, Optional
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class HallucinationPreventionConfig:
"""幻覚防止の設定"""
use_rag: bool = True
verify_output: bool = True
require_sources: bool = True
max_temperature: float = 0.3
enable_self_check: bool = True
human_review_threshold: float = 0.7
class SafeLLMWrapper:
"""幻覚対策を組み込んだLLMラッパー"""
def __init__(self, config: HallucinationPreventionConfig):
self.config = config
self.llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=config.max_temperature)
self.vectorstore = self._setup_vectorstore() if config.use_rag else None
def generate(self, question: str) -> Dict[str, any]:
"""安全な回答生成"""
result = {
"question": question,
"answer": "",
"confidence": 0.0,
"sources": [],
"warnings": [],
"requires_human_review": False
}
try:
# 1. RAGによる情報取得
context = ""
if self.config.use_rag and self.vectorstore:
docs = self.vectorstore.similarity_search(question, k=3)
context = "\n".join([doc.page_content for doc in docs])
result["sources"] = [doc.metadata for doc in docs]
# 2. 構造化プロンプトで回答生成
prompt = self._create_safe_prompt(question, context)
answer = self.llm.invoke(prompt)
result["answer"] = answer
# 3. 自己検証
if self.config.enable_self_check:
verification = self._self_verify(question, answer)
result["confidence"] = verification["confidence"]
result["warnings"] = verification["warnings"]
# 4. 出力検証
if self.config.verify_output:
is_valid = self._verify_facts(answer, context)
if not is_valid:
result["warnings"].append("事実確認で矛盾を検出")
result["confidence"] *= 0.5
# 5. 人間レビューの判定
if result["confidence"] < self.config.human_review_threshold:
result["requires_human_review"] = True
except Exception as e:
result["warnings"].append(f"エラー: {str(e)}")
result["requires_human_review"] = True
return result
def _create_safe_prompt(self, question: str, context: str) -> str:
"""安全なプロンプト生成"""
return f"""
あなたは正確性を最優先する専門家です。
【重要な制約】
1. 提供された情報のみを使用してください
2. 不確実な場合は明示してください
3. {("情報源を引用してください" if self.config.require_sources else "")}
【提供情報】
{context if context else "追加情報なし"}
【質問】
{question}
"""
def _self_verify(self, question: str, answer: str) -> Dict:
"""自己検証を実行"""
# 実装省略
return {"confidence": 0.85, "warnings": []}
def _verify_facts(self, answer: str, context: str) -> bool:
"""事実検証を実行"""
# 実装省略
return True
# 使用例
config = HallucinationPreventionConfig(
use_rag=True,
verify_output=True,
require_sources=True,
max_temperature=0.2,
enable_self_check=True,
human_review_threshold=0.7
)
safe_llm = SafeLLMWrapper(config)
result = safe_llm.generate("当社の最新製品の仕様は?")
print(f"回答: {result['answer']}")
print(f"信頼度: {result['confidence']:.2%}")
print(f"人間レビュー必要: {result['requires_human_review']}")
if result['warnings']:
print(f"警告: {', '.join(result['warnings'])}")モニタリングと継続的改善
幻覚対策は一度実装して終わりではなく、継続的なモニタリングと改善が必要です。
幻覚検出メトリクス
from datetime import datetime
from typing import List
class HallucinationMonitor:
"""幻覚発生のモニタリング"""
def __init__(self):
self.logs = []
def log_generation(
self,
question: str,
answer: str,
confidence: float,
sources: List[str],
verification_passed: bool
):
"""生成結果をログ記録"""
self.logs.append({
"timestamp": datetime.now(),
"question": question,
"answer": answer,
"confidence": confidence,
"sources": sources,
"verification_passed": verification_passed
})
def calculate_metrics(self) -> Dict:
"""メトリクスを計算"""
total = len(self.logs)
if total == 0:
return {}
passed = sum(1 for log in self.logs if log["verification_passed"])
avg_confidence = sum(log["confidence"] for log in self.logs) / total
return {
"total_generations": total,
"verification_pass_rate": passed / total,
"average_confidence": avg_confidence,
"low_confidence_rate": sum(
1 for log in self.logs if log["confidence"] < 0.7
) / total
}
def get_suspicious_cases(self, threshold: float = 0.6) -> List[Dict]:
"""疑わしいケースを抽出"""
return [
log for log in self.logs
if log["confidence"] < threshold or not log["verification_passed"]
]
# 使用例
monitor = HallucinationMonitor()
# 各生成時にログ記録
result = safe_llm.generate("質問内容")
monitor.log_generation(
question="質問内容",
answer=result["answer"],
confidence=result["confidence"],
sources=result["sources"],
verification_passed=len(result["warnings"]) == 0
)
# 定期的にメトリクスを確認
metrics = monitor.calculate_metrics()
print(f"検証通過率: {metrics['verification_pass_rate']:.2%}")
print(f"平均信頼度: {metrics['average_confidence']:.2%}")
# 疑わしいケースをレビュー
suspicious = monitor.get_suspicious_cases()
for case in suspicious:
print(f"要確認: {case['question']}")よくある質問
幻覚を完全に防ぐことはできますか?
現在の技術では、LLMの幻覚を100%防ぐことは困難です。しかし、本記事で紹介した対策を組み合わせることで、幻覚の発生率を大幅に削減できます。
重要なのは、完全に防ぐことを目指すのではなく、以下のアプローチを取ることです:
- 幻覚のリスクを最小化:RAGやプロンプト設計で発生率を下げる
- 幻覚を検出:自動検証や人間レビューで検出
- 影響を限定:ソース引用により、ユーザーが判断できるようにする
RAGを使えば幻覚は発生しませんか?
いいえ、RAGを使用しても幻覚は完全には防げません。以下の理由があります:
- 検索された情報が不完全または関連性が低い場合
- LLMが検索結果を誤解釈する場合
- 複数の情報源から誤った統合をする場合
RAGは幻覚を大幅に削減しますが、万能ではありません。検索品質の向上と、出力検証の組み合わせが重要です。
温度パラメータを0にすれば安全ですか?
温度を0に設定すると、出力はより決定的になり、幻覚のリスクは減少しますが、以下の問題があります:
- 柔軟性の低下:同じ入力に対して常に同じ出力
- 創造性の欠如:文章が硬く、不自然になる場合がある
- 完全な保証はない:温度0でも幻覚は発生する可能性がある
推奨される設定:
- 事実ベースのタスク:温度 0.0 〜 0.2
- バランス型:温度 0.3 〜 0.5
- クリエイティブタスク:温度 0.6 〜 0.9
どの対策が最も効果的ですか?
タスクの種類によって最適な対策は異なりますが、一般的には以下の優先順位が推奨されます:
- RAG統合(最も効果的):信頼できる情報源を提供
- プロンプト設計:実装が容易で即効性がある
- 出力検証:追加の安全層として機能
- ソース引用:透明性を確保
- パラメータ調整:補助的な対策
実務では、これらを 組み合わせて使用 することが最も効果的です。
おわりに
LLMの幻覚問題は、AI活用における最も重要な課題の1つです。本記事で紹介した対策を実装することで、信頼性の高いLLMアプリケーションを構築できます。
重要なポイントは以下の通りです:
- 多層防御:複数の対策を組み合わせる
- 継続的監視:幻覚の発生を検出し、改善を続ける
- 透明性:情報源を明示し、ユーザーが判断できるようにする
- 人間の関与:重要な判断には人間のレビューを入れる
次のステップとして、以下の学習をお勧めします:
- RAGの高度な実装:ハイブリッド検索、リランキング、クエリ拡張
- 評価フレームワーク:幻覚検出の自動評価システム
- ファインチューニング:特定ドメインでの精度向上
私たちShineosでは、信頼性の高いAIシステムの構築を支援しています。幻覚対策を含むLLMアプリケーション開発にご興味がある方は、ぜひお問い合わせください。